Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Vision Behind Starlink
- Development and Launch Timeline
- Technological Innovations
- Impact on Global Connectivity
- Economic Impact
- Challenges and Controversies
- Future Prospects
- Conclusion
Introduction
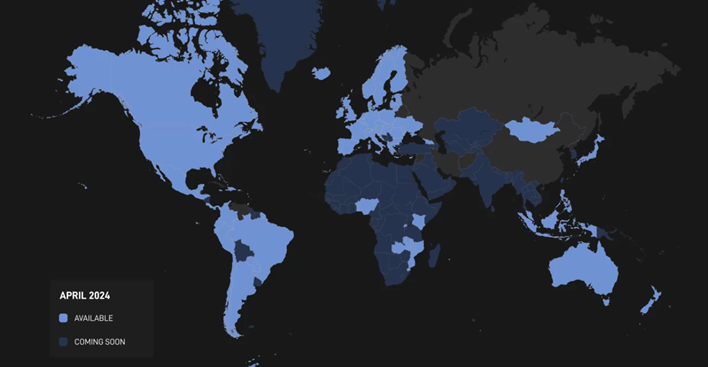
Starlink, operated by Starlink Services, LLC, a subsidiary of SpaceX, is a satellite internet constellation aimed at providing global broadband coverage. Since its start, Starlink has launched thousands of satellites into low Earth orbit (LEO), changing the landscape of global internet connectivity. This marks the 100th country, territory, or other market around the world where Starlink’s high-speed, low-latency internet is available.
The Vision Behind Starlink
SpaceX’s journey to develop Starlink began with the goal of providing high-speed internet to underserved and remote areas worldwide. The idea was to create a network of small satellites that could deliver reliable internet access, reducing the digital divide and connecting many people to the internet.
Development and Launch Timeline
Early Concept and Initial Challenges
The concept of satellite constellations in low Earth orbit dates back to the 1980s. Early attempts by companies like Iridium and Globalstar faced significant financial and technological challenges. These early efforts laid the groundwork for future projects, including Starlink.
Strategic Planning
In 2014, Elon Musk and Greg Wyler explored the potential of a satellite constellation. Although initial plans did not materialize, SpaceX continued to pursue the vision, eventually filing an application with the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) under the name STEAM. By 2016, SpaceX had branded the project as Starlink, inspired by the novel “The Fault in Our Stars.”
Design and Development Phase (2015-2019)
SpaceX officially announced Starlink in January 2015, with a development facility in Redmond, Washington. The focus was on creating a low-cost, high-capacity satellite network. By 2018, the project had expanded significantly, with additional facilities in Irvine, California, dedicated to signal processing and satellite design.
Initial Launches and Growth
The first test satellites were launched in February 2018. By May 2019, SpaceX had successfully launched the first batch of 60 operational Starlink satellites. The company rapidly scaled up its launch cadence, aiming to deploy thousands of satellites to meet regulatory requirements and achieve global coverage.
Technological Innovations
ACCESSORIES & MOUNTS
Available in the Starlink

Starlink’s success is rooted in its technological advancements. Key features include:
- Mass-Produced Satellites: Over 6,000 satellites have been launched, with plans to increase this number significantly.
- Advanced Propulsion Systems: Satellites are equipped with Hall-effect thrusters for efficient orbit management and de-orbiting.
- Autonomous Collision Avoidance: Satellites can autonomously avoid collisions using uplinked tracking data.
- Low-Latency Communication: Positioned in low Earth orbit, Starlink satellites offer low-latency internet, ideal for real-time applications.
Impact on Global Connectivity
Starlink has dramatically improved internet access in remote and underserved regions. With over 3 million subscribers as of May 2024, Starlink provides high-speed internet to users in over 75 countries. The network’s ability to deliver reliable service in areas where traditional infrastructure is lacking has been a game-changer. This milestone marks the availability of Starlink’s high-speed, low-latency internet in 100 countries, territories, or other markets globally.
Economic Impact
Starlink’s economic impact extends beyond providing internet access. Key financial milestones include:
- Initial Investment: Estimated at $10 billion to develop and deploy the constellation.
- Revenue Growth: Expected to reach $6.6 billion in 2024.
- Employment Opportunities: Significant job creation in satellite manufacturing, ground station maintenance, and customer support.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite its successes, Starlink faces several challenges:
- Astronomical Interference: Astronomers have raised concerns about the impact of Starlink satellites on ground-based observations. SpaceX is working on measures to mitigate this issue, such as reducing satellite brightness.
- Orbital Debris: The increasing number of satellites in orbit raises concerns about space debris. SpaceX has implemented de-orbit plans to address this problem.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating international regulations and securing necessary licenses remains a complex task.
Future Prospects
Starlink’s future looks promising, with plans to expand the constellation to 34,400 satellites. This expansion aims to enhance coverage, increase bandwidth, and improve service quality. Additionally, the development of Starshield, a military version of Starlink, indicates potential growth in defense and government sectors.
Conclusion
Starlink represents a significant leap forward in global connectivity. By leveraging advanced satellite technology, SpaceX has created a network that not only bridges the digital divide but also opens up new opportunities for economic and social development. As Starlink continues to evolve, it promises to reshape the way we connect with the world.
Starlink’s Key Features and Specifications
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Launch Year | 2019 |
| Number of Satellites (2024) | 6,000+ |
| Planned Satellites | 12,000 initially, up to 34,400 |
| Orbit Type | Low Earth Orbit (LEO) |
| Internet Speed | Up to 150 Mbps (beta phase) |
| Coverage | Over 75 countries |
| Revenue (2024) | $6.6 billion |
| Initial Investment | $10 billion |
| Subscribers (May 2024) | 3 million |
| Regulatory Body | FCC (Federal Communications Commission) |
Starlink Service Benefits
- Global Coverage: Provides internet access in remote and underserved areas.
- Low Latency: Ideal for real-time applications like gaming and video conferencing.
- Scalable: Plans to expand the constellation for increased capacity and coverage.
- Economic Boost: Generates significant revenue and creates job opportunities.
- Technological Advancement: Pioneers new technologies in satellite communication.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
- Astronomical Interference: Implementing measures to reduce satellite brightness.
- Space Debris: Developing robust de-orbit plans to minimize space debris.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating international regulations and securing licenses.
Future Plans
- Expansion: Increasing the satellite count to enhance service quality and coverage.
- Military Applications: Developing Starshield for government and defense use.
- Innovation: Continuing to innovate in satellite technology and ground infrastructure.
Starlink’s ambitious project has the potential to redefine global internet connectivity. By addressing existing challenges and leveraging technological advancements, SpaceX aims to create a more connected world, providing high-speed internet to even the most remote corners of the globe. This milestone marks the availability of Starlink’s high-speed, low-latency internet in 100 countries, territories, or other markets globally.








Leave a Reply